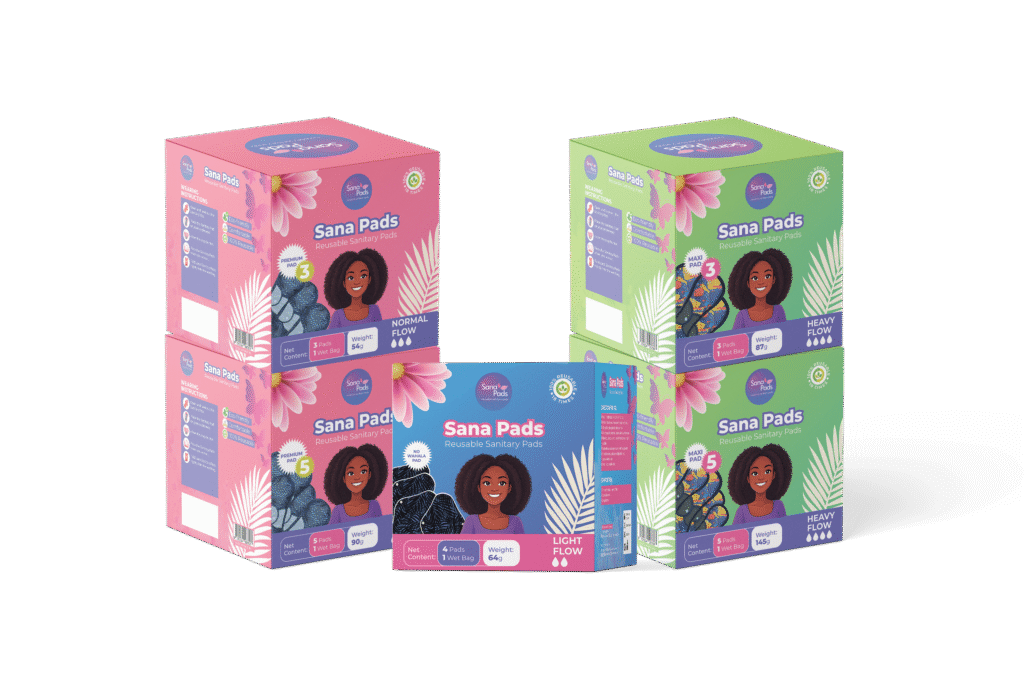
How to Include Reusable Pads in Your CSR or ESG Strategy: A Practical Guide for Nigerian Organizations
Imagine walking into a secondary school in Lagos where girls no longer miss classes during their periods. Picture a workplace where female employees feel supported and valued throughout their menstrual cycles. This transformation isn’t just a dream—it’s happening across Nigeria through innovative CSR and ESG programs that prioritize menstrual health.
At Sana Pads, we’ve witnessed firsthand how organizations can create lasting impact while meeting their sustainability goals. Moreover, the integration of menstrual health into corporate strategies represents one of the most cost-effective ways to advance gender equality and environmental protection simultaneously.
Why Menstrual Health Belongs in Your CSR Strategy
The Scale of Period Poverty in Nigeria
In Nigeria, approximately 50 million women and girls lack reliable access to hygienic menstrual products. Consequently, many resort to unsafe alternatives like rags, newspapers, or leaves—materials that can cause serious infections and health complications. Furthermore, this challenge extends beyond individual health, affecting entire communities and economic development.
The financial burden of menstruation creates additional barriers. When families earn between ₦30,000 and ₦50,000 monthly, spending ₦2,000-₦3,000 on disposable pads becomes prohibitive. As a result, girls often stay home during their periods, missing up to 20% of their school days annually.
Organizations like Plan International Nigeria have documented how period poverty directly correlates with educational dropout rates. Similarly, WaterAid Nigeria reports that inadequate menstrual hygiene facilities in schools compound these challenges.
How Menstrual Health Connects to Multiple SDGs
Addressing menstrual health through your CSR strategy simultaneously advances several Sustainable Development Goals:
SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being)
Providing safe menstrual products reduces infections and promotes reproductive health. Additionally, education about menstrual hygiene builds lifelong healthy practices.
SDG 4 (Quality Education)
When girls have access to reliable menstrual products, their school attendance improves dramatically. Moreover, dignity and comfort during menstruation enhance their learning experience.
SDG 5 (Gender Equality)
Menstrual equity programs directly challenge period poverty and stigma. Furthermore, they create opportunities for women’s economic participation and leadership.
SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation)
Reusable pad programs often include improved WASH facilities and hygiene education. Consequently, entire communities benefit from better sanitation practices.
How it works
At Sana Pads, we use carefully selected materials to ensure comfort and reliability. Each pad includes a leak-proof layer for maximum protection and bamboo fibers for superior absorbency. Unlike polyester, bamboo is naturally odor-resistant and gentle on the skin, keeping you comfortable and fresh throughout the day. Our pads provide dependable, eco-friendly protection you can count on.
Production
Sana Pads are produced in Nigeria and are compliant with NAFDAC requirements.
All pads are inspected by our quality control team and afterwards sanitized before they are sold.

Sana Pads are designed for easy care without a washing machine. After use, simply rinse the pad in water, then hand wash with a mild soap.
For freshness and hygiene, sun-dry Sana Pads after washing. The sun’s UV rays naturally disinfect and remove odors, keeping your pads soft and ready for reuse. It’s an easy, eco-friendly drying method that ensures long-lasting comfort.
Sustainable, chemical-free, low-cost & low stress
Sana Pads are crafted to be sustainable, safe, affordable, and easy to use. Made from eco-friendly materials, they’re designed for reusability, helping you reduce waste. Free from harsh chemicals, they’re gentle on the skin, offering comfort without irritation. Their reusable nature keeps costs low, making them a smart, long-lasting choice for your cycle.
The Business Case for Menstrual Equity Programs
Beyond social impact, menstrual health programs deliver measurable business benefits. Employee productivity increases when women feel supported during menstruation. Additionally, companies implementing these programs report improved retention rates and enhanced employer brand reputation.
The Nigeria Private Sector Alliance (NIPSA) has highlighted how workplace menstrual health support contributes to gender-inclusive environments. Furthermore, these initiatives position organizations as progressive employers, attracting top talent.
Environmental Impact: Meeting Your ESG Goals
The Plastic Problem with Disposable Pads
Traditional disposable pads contain plastic components that take 500-800 years to decompose. In Nigeria alone, approximately 50 million women generate millions of tons of menstrual waste annually. Consequently, this creates an environmental crisis that organizations can no longer ignore.
Each woman using disposable products creates roughly 5.5 kg of menstrual waste per year. Multiplied across Nigeria’s female population, this represents a staggering environmental burden. Moreover, improper disposal in water bodies and open dumps exacerbates pollution challenges.
The Nigerian Environmental Society has documented how menstrual waste contributes to plastic pollution in waterways. Similarly, environmental research shows that decomposing disposable pads release harmful chemicals into soil and groundwater.
How Reusable Pads Support Climate Goals
Switching to reusable pads dramatically reduces carbon footprint and waste generation. One reusable pad replaces approximately 100-200 disposable alternatives over its 3-year lifespan. Therefore, organizations implementing reusable pad programs can quantify significant environmental impact.
Manufacturing reusable pads locally, like those produced by Sana Pads, further reduces transportation emissions. Additionally, supporting local production creates employment opportunities while minimizing environmental impact.
Research from UNICEF Nigeria indicates that reusable menstrual products can reduce individual carbon footprints by up to 85% compared to disposables. Furthermore, the environmental savings compound when programs reach thousands of beneficiaries.
Measuring Environmental ROI
Organizations can track their environmental impact through several metrics:
- Plastic waste diverted: Calculate kilograms of disposable pad waste prevented
- Carbon emissions reduced: Measure transportation and manufacturing emissions saved
- Water conservation: Quantify water saved in disposable pad production
- Landfill diversion: Track waste volumes redirected from disposal sites
These measurements provide concrete data for ESG reporting and stakeholder communication. Moreover, they demonstrate your organization’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
Our Reusable Sanitary Pads
Light Flow
Thinner and ligher pad designed for
the last days of your period.
Contains leakproof layer at the back.
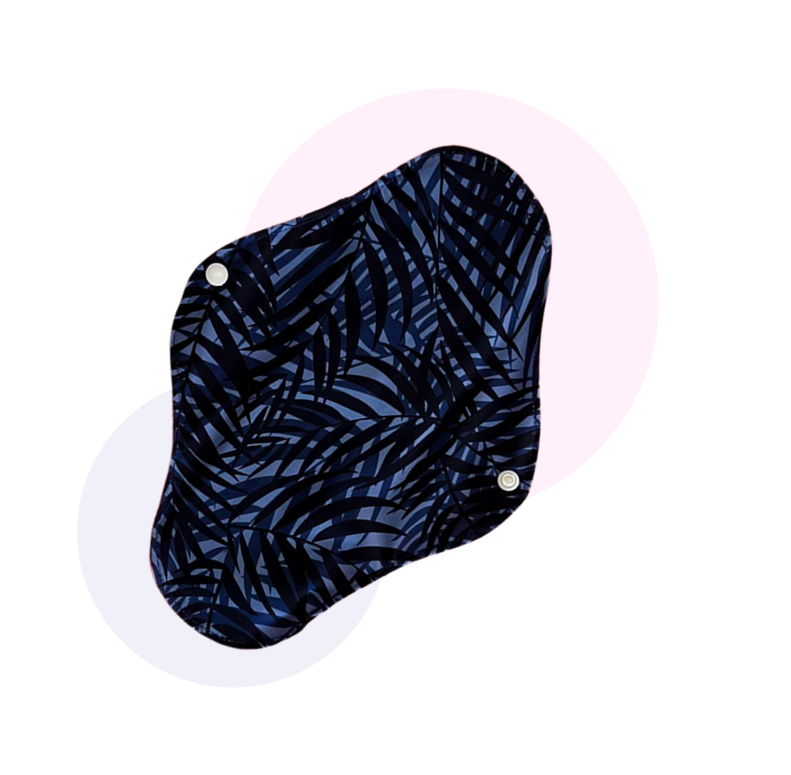

Normal Flow
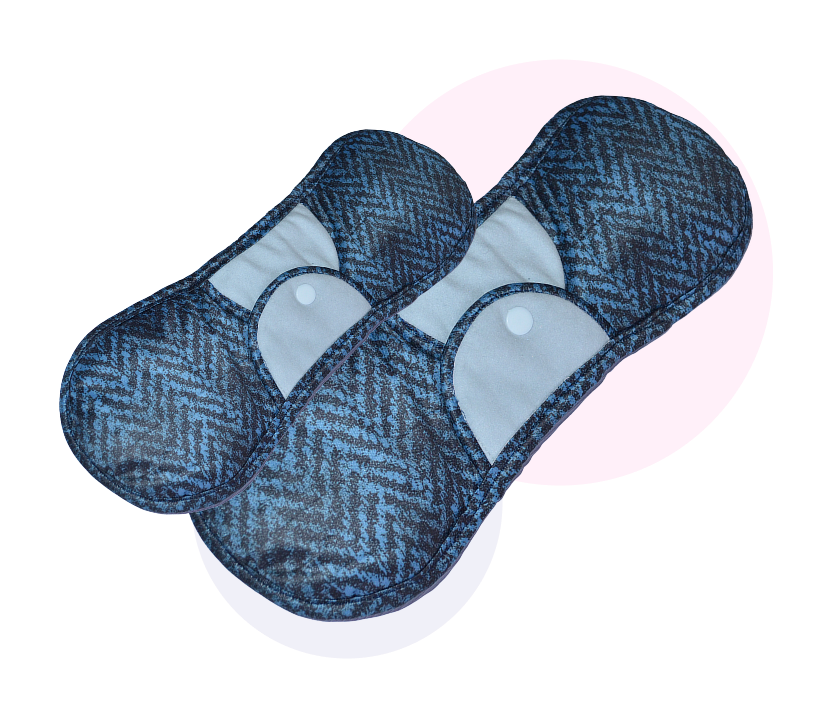

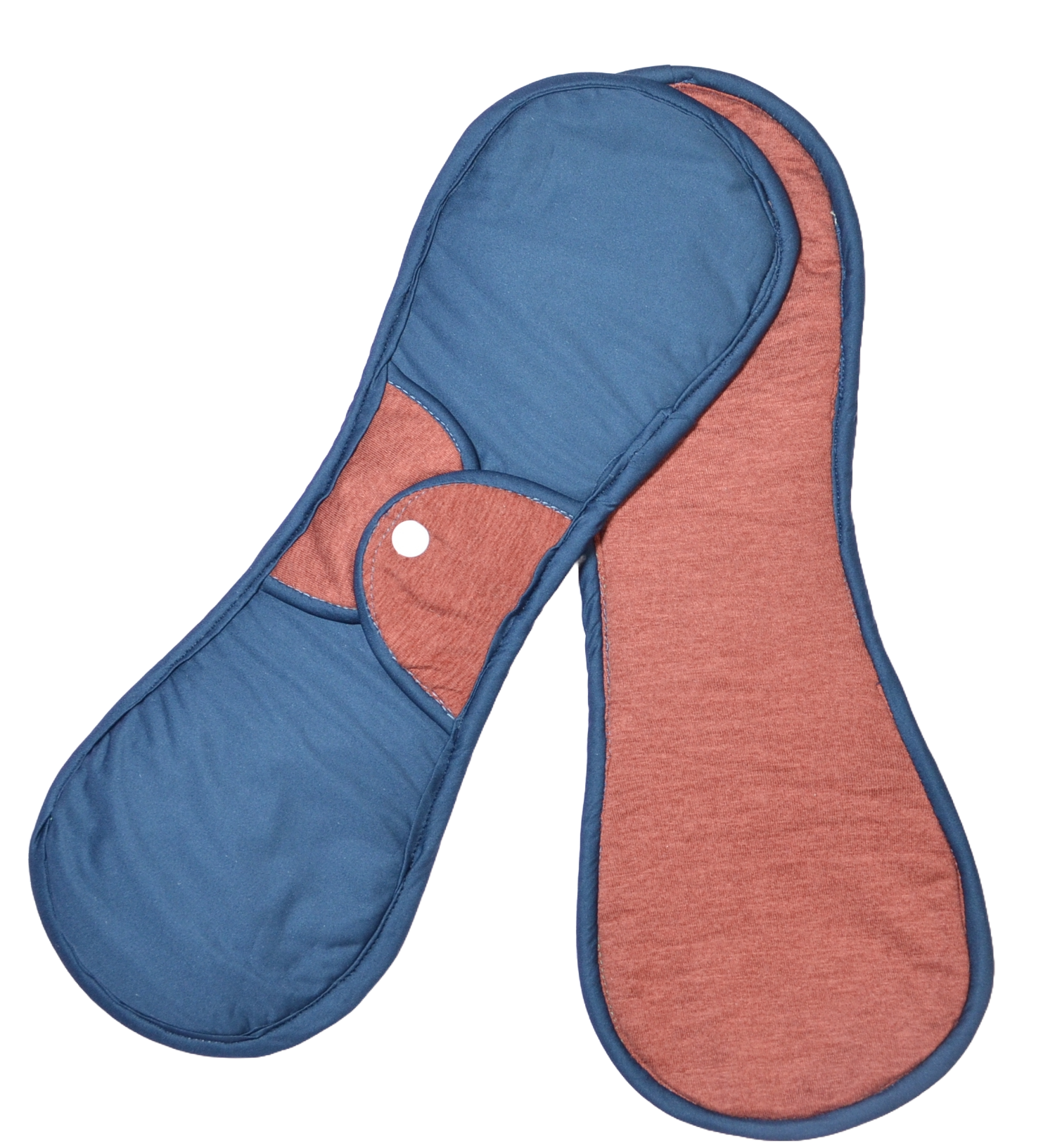
Social Impact: Empowering Women and Girls
Breaking the School Dropout Cycle
Education transforms lives, yet period poverty creates barriers that keep girls out of classrooms. When organizations provide reusable pads to schools, they directly address this challenge. Consequently, girls gain confidence, improve attendance, and achieve better academic outcomes.
The Federal Ministry of Education Nigeria has recognized menstrual health as crucial for achieving educational equity. Additionally, state governments are increasingly integrating menstrual hygiene into school health programs.
Success stories from schools using Sana Pads demonstrate remarkable improvements. For instance, attendance rates increase by 25-40% when girls have reliable access to quality menstrual products. Furthermore, teachers report enhanced classroom participation and academic performance.
Supporting Women's Economic Participation
Workplace menstrual health programs create enabling environments for women’s professional growth. When employers provide reusable pads and supportive policies, female employees experience less stress and greater job satisfaction. Consequently, organizations benefit from improved productivity and reduced absenteeism.
The International Labour Organization Nigeria emphasizes how menstrual health support contributes to decent work conditions. Moreover, these programs signal organizational commitment to gender equality and inclusion.
Local manufacturing of reusable pads also creates employment opportunities, particularly for women. For example, Sana Pads employs local seamstresses and provides skills training, demonstrating how CSR programs can generate economic empowerment.
Building Healthier Communities
Menstrual health education programs create ripple effects throughout communities. When organizations support comprehensive menstrual hygiene initiatives, they contribute to breaking stigma and promoting health awareness. Subsequently, entire families and communities benefit from improved knowledge and practices.
Community health workers trained in menstrual hygiene become advocates for women’s health broadly. Additionally, these programs often include mothers and caregivers, extending impact beyond direct beneficiaries.
Practical Implementation: Getting Started
Partnering with Local Manufacturers (like Sana Pads)
Successful menstrual health programs require reliable, high-quality products that meet users’ needs. Partnering with established local manufacturers ensures product quality while supporting domestic economic development. Furthermore, local partnerships enable customization and responsive service delivery.
Sana Pads offers comprehensive partnership packages for organizations implementing CSR programs. These include product supply, training materials, monitoring tools, and ongoing technical support. Additionally, our team provides guidance on culturally appropriate implementation strategies.
Key considerations for manufacturer partnerships include:
- Product quality standards: Ensure pads meet international hygiene and safety requirements
- Production capacity: Verify ability to meet your program’s scale and timeline
- Local presence: Choose manufacturers with community connections and cultural understanding
- Support services: Select partners offering training, education, and monitoring assistance
Distribution Models That Work
Effective distribution requires careful planning and community engagement. Successful models include:
School-based programs: Partnering with education authorities to integrate menstrual health into school health services. Consequently, girls receive products, education, and ongoing support in familiar environments.
Health facility integration: Working with clinics and health centers to include menstrual products in reproductive health services. Moreover, this approach ensures medical oversight and broader health education.
Workplace programs: Providing products and education directly to female employees through HR departments. Additionally, these programs can include supportive policies like menstrual leave.
Community distribution: Engaging local women’s groups and community organizations for peer-to-peer education and support. Furthermore, this model leverages existing social networks and trust relationships.
Training and Education Components
Product distribution alone isn’t sufficient—comprehensive education ensures program success. Essential training components include:
Product usage: Detailed instruction on wearing, changing, and caring for reusable pads. Additionally, troubleshooting common concerns and questions.
Hygiene practices: Broader menstrual hygiene education covering body changes, health monitoring, and when to seek medical care. Moreover, addressing myths and misconceptions that may create barriers.
Maintenance and care: Proper washing, drying, and storage techniques to maximize product lifespan. Furthermore, teaching repair skills to extend usability.
Peer education: Training participants to share knowledge with friends, family, and community members. Consequently, program impact multiplies through informal networks.
Organizations like Society for Family Health Nigeria have demonstrated how comprehensive education enhances program effectiveness. Similarly, Marie Stopes International Nigeria emphasizes the importance of combining products with knowledge and support.
Time to get involved
Measuring Success: KPIs and Reporting
Tracking Social Impact Metrics
Robust monitoring systems enable organizations to demonstrate program effectiveness and make data-driven improvements. Key social impact indicators include:
Educational outcomes:
- School attendance rates before and after program implementation
- Academic performance improvements among beneficiaries
- Dropout rate reductions in target schools
Health improvements:
- Reported infections and health complications
- Healthcare seeking behaviors
- Overall reproductive health knowledge
Empowerment indicators:
- Self-confidence assessments among participants
- Leadership opportunities and participation
- Economic activity and entrepreneurship among beneficiaries
Environmental Impact Measurement
Environmental metrics provide concrete evidence of sustainability contributions:
Waste reduction:
- Kilograms of disposable pad waste prevented annually
- Percentage reduction in menstrual waste generation
- Landfill diversion rates
Carbon footprint:
- CO2 emissions reduced through local manufacturing
- Transportation emissions saved
- Lifecycle carbon footprint comparisons
Resource conservation:
- Water saved in manufacturing processes
- Raw material consumption reductions
- Energy efficiency improvements
ESG Reporting Best Practices
Effective ESG reporting communicates impact clearly to stakeholders while demonstrating organizational commitment. Best practices include:
Quantitative data: Present concrete numbers showing program reach, environmental savings, and social outcomes. Additionally, use visual representations like charts and infographics to enhance understanding.
Qualitative stories: Include personal testimonials and case studies that illustrate program impact on individual lives. Moreover, these narratives humanize data and create emotional connections with stakeholders.
Comparative analysis: Show improvements over time and benchmark against industry standards or similar programs. Furthermore, this demonstrates continuous improvement and organizational learning.
Third-party validation: Engage independent evaluators or partner with research institutions to verify impact claims. Consequently, this enhances credibility and builds stakeholder trust.
Real Success Stories from Nigerian Organizations
Corporate Programs That Made a Difference
Leading Nigerian companies have implemented innovative menstrual health programs with remarkable results. For instance, a major telecommunications company partnered with Sana Pads to provide reusable products to female employees across their offices. Subsequently, they reported 30% reduction in sick leave requests and improved workplace satisfaction.
Similarly, a multinational bank integrated menstrual health support into their diversity and inclusion strategy. Their program includes product provision, education sessions, and supportive policies. Consequently, female employee retention increased by 15% in the first year.
NGO Partnerships and Their Results
Non-governmental organizations have pioneered community-based menstrual health programs across Nigeria. ActionAid Nigeria has implemented school-based programs reaching thousands of girls in rural communities. Their partnership with local manufacturers ensures sustainable product supply while supporting economic development.
The Centre for Girls’ Education has documented significant improvements in educational outcomes through their menstrual health initiatives. Moreover, their programs include comprehensive sexuality education and life skills training.
Government Initiatives Leading Change
State governments are increasingly recognizing menstrual health as a public health priority. Lagos State’s school health program now includes menstrual hygiene education and product provision. Additionally, the Federal Capital Territory has piloted reusable pad programs in public schools.
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control has developed guidelines for menstrual hygiene in emergency settings, recognizing the importance of dignified menstrual care during crises. Furthermore, these guidelines inform humanitarian response and development programs.
Testimonials
Women around the world patronize Sana

“Buying disposable pads every month really added up, so I thought I’d give Sana Pads a try. I was surprised by how soft they are, and they work well for long days at university.
Washing them is simple, and I haven’t had to buy new pads in months, which has saved me money. I also like that they’re more eco-friendly. It feels good to have an option that’s both affordable and better for the environment.”
Women around the world patronize Sana

At first I felt irritated using a washable sanitary pads,I decided to give it a try and to my greatest surprise,it was very comfortable and very easy to wash, you can even go about your daily activities without fear of getting blood stain in public, I wanna say a Big shout out to SANA PADS!!
Divine Favour Eweka
Women around the world patronize Sana

I’ve tried several pad brands over the years, but Sana pads truly stands out. From the first use, I noticed the difference — soft on the skin, super absorbent, and incredibly comfortable. Even on my heaviest flow days, Sana pads holds up so well. What I also love is how breathable and skin-friendly the material is. If you’re looking for a pad that combines comfort, reliability, and quality, I highly recommend giving Sana pads a try.
Racheal Tarttive
Women around the world patronize Sana

I’m absolutely loving Sana reusable pads! They make me feel so relaxed and at ease during my periods. Plus, they’ve significantly reduced the cost and stress of buying disposable pads every month. Kudos to Sana for creating such an amazing product – I’m a forever fan!
Florence Kigbu
Women around the world patronize Sana

Sana Pad is very good, makes u feel comfortable and free, i love the pads the best ever!.
Susan Eweka
Women around the world patronize Sana

Sana pads have been a game-changer for me! Comfortable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective, they’ve given me confidence and peace of mind during my periods. No more worries about leaks or waste – Sana’s got me covered! Highly recommend!
Blessing Augustine David
Women around the world patronize Sana

I’ve tried several reusable pad brands, but Sana stands out for its exceptional quality, comfort, and durability. The design is thoughtful, and the materials are gentle on my skin. Switching to Sana has not only reduced my environmental footprint but also saved me money in the long run. I’m grateful for this sustainable solution!
Blessing Madubuike
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Addressing Cultural Sensitivities
Menstruation remains a sensitive topic in many Nigerian communities, requiring careful navigation of cultural norms and beliefs. Successful programs invest in community engagement and work with traditional and religious leaders to build acceptance.
Strategies for cultural sensitivity include:
Community dialogue: Organizing discussions with parents, teachers, and community leaders to address concerns and build support. Additionally, these conversations help identify cultural barriers and solutions.
Religious engagement: Working with faith-based organizations to frame menstrual health within religious teachings about cleanliness and health. Moreover, religious leaders can become powerful advocates for program acceptance.
Gradual implementation: Starting with smaller pilot programs to demonstrate benefits before scaling up. Consequently, success stories from early adopters help convince skeptical community members.
Local champions: Identifying and training community members to advocate for menstrual health programs. Furthermore, peer influence often proves more effective than external messaging.
Ensuring Program Sustainability
Long-term success requires sustainable financing and institutional commitment. Organizations must plan beyond initial implementation to ensure continued impact.
Sustainability strategies include:
Local capacity building: Training community members and institutions to manage programs independently. Additionally, this reduces dependence on external support while building local expertise.
Cost-sharing models: Gradually transitioning from full sponsorship to participant contributions, ensuring programs remain accessible while building ownership. Moreover, this approach promotes long-term financial sustainability.
Government integration: Working with public sector partners to incorporate menstrual health into official policies and budgets. Consequently, programs gain institutional support and continued funding.
Income generation: Creating opportunities for beneficiaries to earn income through program activities, such as peer education or product distribution. Furthermore, this enhances individual empowerment while supporting program sustainability.
Budget Planning and Cost Management
Effective financial planning ensures programs achieve maximum impact within available resources. Key considerations include:
Total cost of ownership: Calculating all program costs including products, training, distribution, and monitoring. Additionally, consider indirect costs like staff time and administrative overhead.
Cost per beneficiary: Comparing different implementation models to identify the most cost-effective approaches. Moreover, this analysis helps optimize resource allocation and program design.
Economies of scale: Leveraging bulk purchasing and standardized approaches to reduce unit costs. Furthermore, larger programs often achieve better cost efficiency than smaller initiatives.
Local sourcing: Partnering with domestic manufacturers to reduce costs while supporting local economic development. Consequently, this approach delivers both financial and social benefits.
Next Steps: Building Your Menstrual Health Program
Assessment and Planning Phase
Before launching a menstrual health program, conduct thorough assessment to understand needs, challenges, and opportunities. This includes:
Needs assessment: Survey target beneficiaries to understand current practices, challenges, and preferences. Additionally, engage stakeholders including parents, teachers, and community leaders.
Resource mapping: Identify available resources including funding, partnerships, and implementation capacity. Moreover, assess potential challenges and risk mitigation strategies.
Program design: Develop detailed implementation plans including timelines, budgets, and monitoring frameworks. Furthermore, ensure plans align with organizational goals and beneficiary needs.
Stakeholder engagement: Build relationships with key partners including government agencies, NGOs, and community organizations. Consequently, strong partnerships enhance program effectiveness and sustainability.
Implementation Timeline
Successful program implementation follows a structured timeline:
Months 1-2: Partnership Development
- Finalize manufacturer partnerships and product specifications
- Complete stakeholder agreements and memorandums of understanding
- Develop training materials and monitoring tools
Months 3-4: Pilot Implementation
- Launch small-scale pilot programs in selected locations
- Conduct initial training sessions and product distribution
- Begin monitoring and evaluation activities
Months 5-6: Program Optimization
- Analyze pilot results and incorporate lessons learned
- Refine implementation processes and materials
- Prepare for scaled implementation
Months 7-12: Scale-Up and Evaluation
- Expand program to full target population
- Implement comprehensive monitoring and evaluation
- Document results and prepare impact reports
Long-term Sustainability Strategies
Building sustainable programs requires ongoing commitment and adaptive management:
Continuous improvement: Regularly review and update programs based on monitoring data and beneficiary feedback. Additionally, stay current with best practices and innovations in menstrual health.
Capacity development: Invest in training local partners and building institutional capacity for program management. Moreover, this ensures programs can continue even as organizational priorities evolve.
Policy advocacy: Work with government partners to integrate menstrual health into official policies and programs. Consequently, this creates systemic change that extends beyond individual organizational efforts.
Innovation and adaptation: Remain open to new approaches, technologies, and partnerships that can enhance program effectiveness. Furthermore, innovation drives continuous improvement and impact maximization.
Get Support from the Sana Team
Ready to transform your CSR strategy with meaningful menstrual health programming? Sana Pads offers comprehensive consultation and support for organizations implementing reusable pad programs. Our experienced team provides everything from needs assessment to impact evaluation, ensuring your program achieves maximum social and environmental impact.
Contact us today to discuss how we can partner with your organization to create lasting change for women and girls across Nigeria. Together, we can build a future where no girl misses school because of her period, and no woman faces barriers to economic participation due to inadequate menstrual health support.
Visit our team page to learn more about our CSR collaboration opportunities, or explore our impact stories to see how other organizations have successfully implemented menstrual health programs with Sana Pads.

Author: Margaret Ochegbudu

